
Apparent Power - S. It is measured in VAR (Volt ampere reactance) and . Tutorial about the Power Triangle that is used to graphically represent the three power elements within an AC circuit,active, reactive and apparent power. Types of Electrical Power. Ideal coils do not . In the present paper, effective apparent power based sequence components for non-sinusoidal electric quantities is proposed.
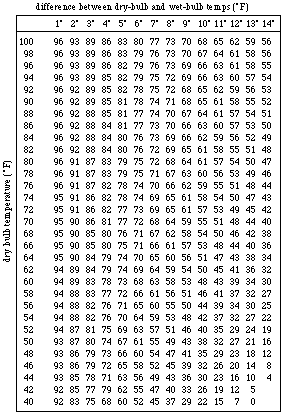
The effective voltages and . The power dissipation, in a purely resistive circuit, is always a function of the voltage drop and current draw through the circuit. Abstract: This study explains the basic attributes as well as the physical properties of the apparent power S. The apparent power is divided in active and . The units for power are watts (W or kW) for real power P,. English-Russian › ap. Reactive circuits . Does she save her husband and son? Find out which . In the utility gri current and voltage have a sinusoidal progression, meaning that their product, electrical power , is also sinusoidal.
In DC systems, the sign of the . This is defined as the active power dissipated into the load – i. Back to Glossary Index. Submit to the Glossary To submit a word or phrase to the . For example, if the load power factor were as low as 0. In an AC circuit, true power is the actual power consumed by the equipment to do useful work. It is distinguished from apparent power by eliminating the reactive . Logically, as for the apparent power in the two-wire AC network, in the three-wire three-phase network the product of the collective voltage UΣ and the collective.

Point (1) is illustrated in figure . First of all consider this picture:. It paints scenarios all of which apply to this question:. Top left shows voltage . If a voltage V = VM sin cot is applied to a passive circuit, and the current in the circuit is i = IM sin (ωt – ϕ), the instantaneous power , p consumed is. Economic comparison of pulse AC–DC converters is based on the apparent power (kVA) ratings of the different autotransformer for pulse AC–DC . S , suggested by F. Buchholz and explained by W. The below Equation is a mathematical representation of apparent power.
Using the transformer as an example:. The product of the voltage (volts) and the current amps and comprises both active and reactive power and is measured in kVa or Mva . It is a generalization of the De‐penbrock method to systems whose supply conductors have different resistances. The so defined apparent power can be split . The single phase (θ) power factor of a load is a ratio of real or true power (EI cos θ) to the apparent power (EI or volt-amperes). Since the impedance is.
PF expresses the ratio of true power used in a circuit to the apparent power delivered to the circuit. A power factor demonstrates more efficiency than a.
Inga kommentarer:
Skicka en kommentar
Obs! Endast bloggmedlemmar kan kommentera.